In modern workspaces, healthcare environments, and commercial facilities, sound masking systems have become essential to maintaining speech privacy and minimizing distractions. But achieving the right acoustic balance depends on more than just high-quality equipment — it’s about how and where the speakers are placed. This includes understanding how ceiling speaker coverage, office acoustics, and speaker placement affect sound waves, reflected sound, and overall listening experience.
At Lencore, every element of system design — from coverage diameter to speaker orientation — is engineered to create uniform, comfortable sound masking that enhances focus and privacy across the entire workspace. Our approach takes office space conditions, ceiling height, reflective surfaces, and ambient noise into account to significantly improve acoustic comfort.
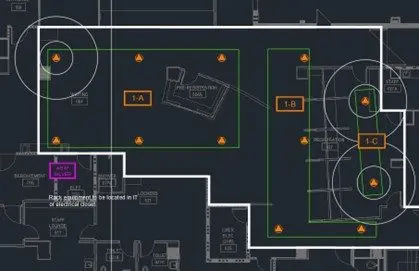
Understanding Coverage Diameter
Each Lencore speaker model has a defined coverage area that ensures consistent sound levels throughout a space:
Direct-fired speakers: ~12 ft. diameter of coverage
Indirect-fired speakers: ~15 ft. diameter of coverage
These guidelines help determine the appropriate number of speakers and their layout across the ceiling grid. Proper coverage prevents “hot spots” (too loud) and “cold spots” (too quiet), ensuring a smooth, seamless masking field.
This even dispersion helps control background noise, sound reflections, and direct sound to create better office acoustics.
To maintain even sound distribution, speakers should be spaced approximately 12-15 feet on-center, allowing their dispersion patterns to overlap and blend smoothly. Each speaker projects sound in a 120° conical pattern, which ensures uniform masking and maintains consistent sound pressure levels (SPL) across the workspace.
This overlap technique supports ideal ceiling speaker coverage.
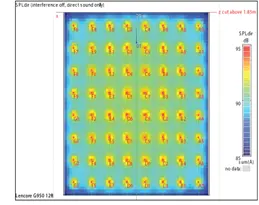
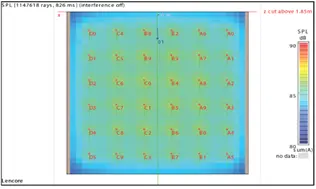
Speaker Orientation: A Crucial Design Factor
One of the most important — and often overlooked — aspects of sound masking system performance is speaker orientation in relation to the plenum space (the air cavity above a drop ceiling). Speaker orientation directly influences sound energy, room acoustics, and listening position clarity.
When the Plenum is Less Than 6 Feet Deep
Speakers should be oriented upward toward the hard deck.
This configuration allows the sound to reflect off the ceiling deck and diffuse evenly throughout the plenum before passing through the ceiling tiles into the workspace. The result: a non-localizable, balanced sound field with excellent uniformity.
This method uses reflected sound to create ambient sound that supports comfortable office acoustics and reduces noticeable sound sources.
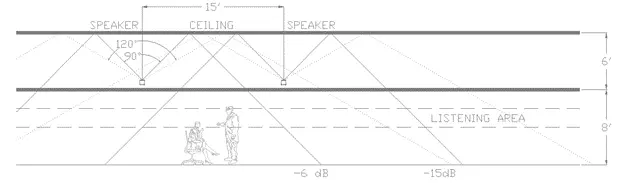
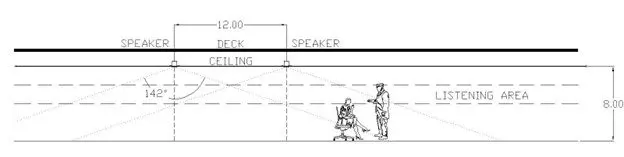
When the Plenum is Greater Than 6 Feet Deep
Speakers should be oriented downward toward the occupied space.
In deeper plenums, upward-facing speakers cause sound to dissipate unevenly, leading to inconsistent masking levels. Downward orientation ensures sound energy is directed efficiently into the workspace, preserving clarity and even coverage.
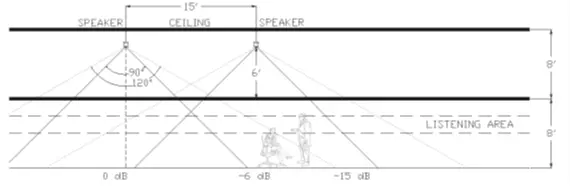
In a Standard Ceiling without a Plenum Space
Speakers should be oriented downward toward the occupied space.
With a standard 8-foot ceiling, direct-fired speakers sit only about 2 feet above a standing person and 4 feet above a seated person. Because the –6 dB rated coverage angle (100°) cannot be achieved without extremely tight spacing of 4–6 feet, the practical approach is to space speakers approximately 12 feet apart. This layout provides effective coverage with fewer speakers and is typically used for paging rather than sound masking.
Why It Matters
Proper speaker orientation and spacing create a diffuse, non-directional sound field the hallmark of effective sound masking. Whether the goal is privacy in a financial office, comfort in a healthcare environment, or focus in an open-plan workspace, these placement principles make all the difference. Maintaining consistent ceiling speaker coverage and improving office acoustics ensures uniform sound behavior across the workspace. These principles also support proper speaker orientation and reduce common issues like sound reflections and ambient noise.
Learn how our sound masking systems enhance privacy and acoustic performance.
Key acoustic benefits include:
- Even diffusion and uniformity – Prevents noticeable speaker sources
- Optimal energy use – Reduces wasted sound in large air volumes
- Improved masking consistency – Maintains comfortable SPL at 4–6 feet (the listener’s ear level)
The Lencore Advantage
Lencore’s systems are designed with both engineering precision and human comfort in mind. Our team provides complete layout and design support to help integrators achieve the perfect balance of speaker spacing, coverage, and orientation for every environment.
This includes optimizing ceiling speaker coverage, evaluating office acoustics conditions, and ensuring proper speaker orientation for uniform acoustic performance.
Work with Lencore’s experts to ensure your next sound masking project achieves optimal coverage, privacy, and acoustic comfort. Submit a request for a free design and quotation today!
